Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) is a complex group of bone marrow disorders in which the body fails to produce healthy, functional blood cells. Accurate diagnosis and thorough evaluation are critical for determining disease severity, prognosis, and whether stem cell therapy may be an appropriate treatment option. At advanced medical centers like Liv Hospital, a multidisciplinary approach ensures precise diagnosis using state-of-the-art diagnostic tools and internationally recognized evaluation protocols.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of how stem cell–related Myelodysplastic Syndrome diagnosis and evaluation are performed, helping patients and caregivers better understand each step of the process.
Understanding Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS)
Myelodysplastic Syndrome occurs when abnormal stem cells in the bone marrow produce immature or defective blood cells. These abnormal cells often die early or function poorly, leading to low levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Over time, MDS may progress to acute myeloid leukemia (AML), making early and accurate evaluation essential.
Patients may experience symptoms such as fatigue, frequent infections, easy bruising, or unexplained bleeding. However, in early stages, MDS can remain asymptomatic and is often detected through routine blood tests.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis in Stem Cell MDS
Diagnosis of Myelodysplastic Syndrome is not based on a single test. Instead, it involves a series of clinical evaluations, laboratory tests, and bone marrow analyses to confirm the condition and determine its risk category.
A detailed diagnostic process helps physicians:
- Confirm the presence of MDS
- Identify specific MDS subtypes
- Assess eligibility for stem cell therapy
- Estimate disease progression and survival outcomes
- Design personalized treatment strategies
Initial Clinical Evaluation and Medical History
The diagnostic journey typically begins with a comprehensive clinical evaluation. Physicians review the patient’s medical history, symptoms, prior chemotherapy or radiation exposure, family history of blood disorders, and any underlying medical conditions.
Physical examination may reveal signs such as pallor, enlarged spleen, bruising, or infections, which can provide early clues supporting further investigation.
Blood Tests and Laboratory Investigations
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
A complete blood count is usually the first diagnostic test performed. It often shows:
- Anemia (low red blood cell count)
- Neutropenia (low white blood cell count)
- Thrombocytopenia (low platelet count)
Abnormalities in cell size, shape, and maturity raise suspicion for MDS.
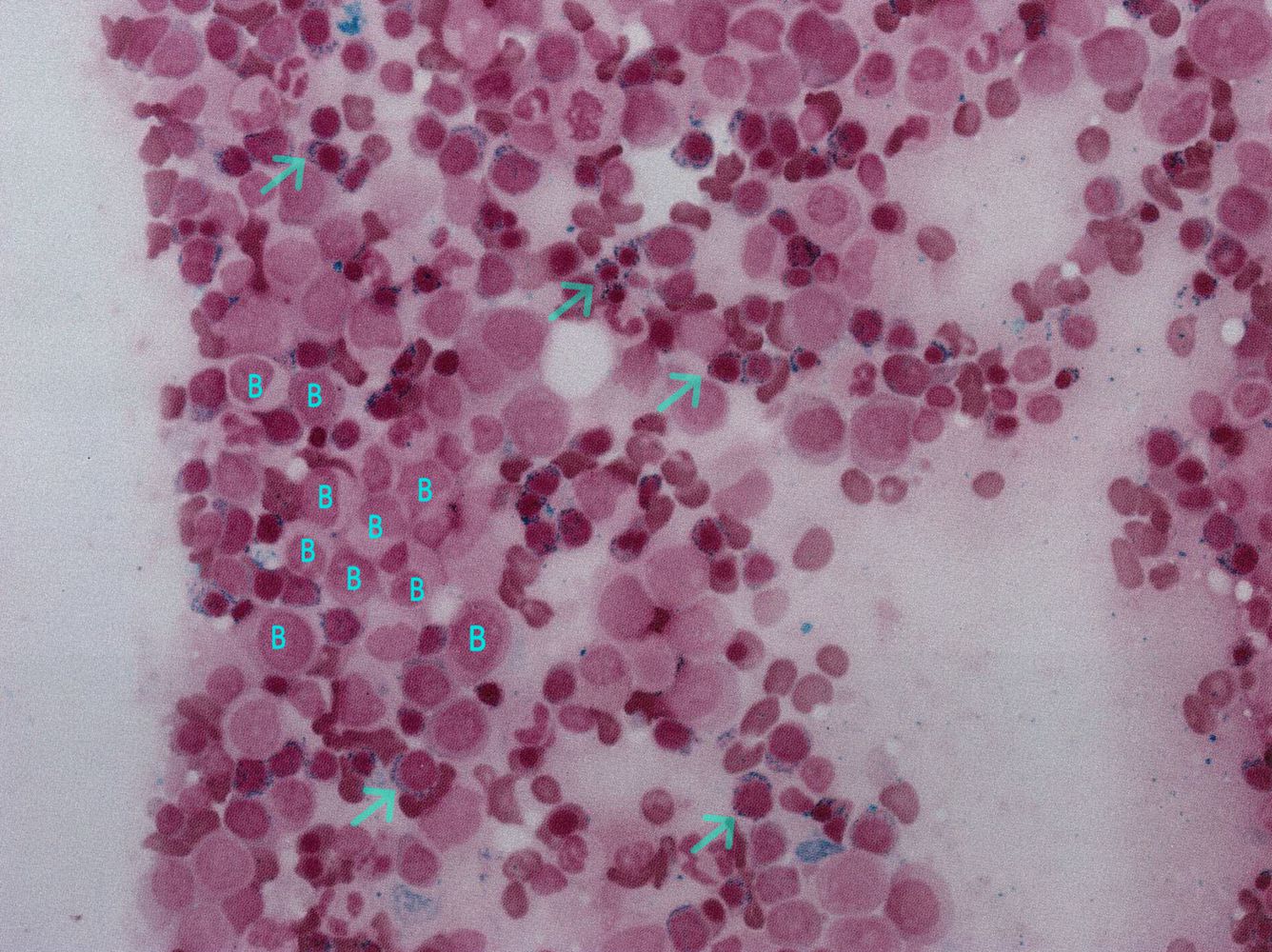
Peripheral Blood Smear
A microscopic examination of blood cells helps identify dysplastic (abnormally formed) cells. This test provides visual evidence of impaired blood cell development.
Bone Marrow Examination: The Diagnostic Cornerstone
Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy
A bone marrow biopsy is essential for confirming Myelodysplastic Syndrome. This procedure allows specialists to evaluate:
- Bone marrow cellularity
- Presence of abnormal stem cells
- Percentage of blast cells
- Degree of dysplasia across blood cell lines
The biopsy results play a key role in determining whether a patient is a candidate for stem cell–based treatment approaches.
Cytogenetic and Molecular Testing
Chromosomal Analysis (Cytogenetics)
Cytogenetic testing examines chromosomes within bone marrow cells to identify genetic abnormalities. Certain chromosomal changes are strongly associated with MDS prognosis and treatment response.
Molecular and Genetic Testing
Advanced molecular tests detect specific gene mutations that influence disease behavior. These findings help stratify patients into risk categories and guide decisions regarding stem cell transplantation.
Risk Stratification and Prognostic Scoring Systems
Once diagnostic data is collected, physicians use standardized scoring systems such as the International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) or its revised version (IPSS-R). These systems evaluate:
- Blood cell counts
- Bone marrow blast percentage
- Cytogenetic abnormalities
Risk classification is essential for determining whether stem cell therapy is recommended as an early intervention or reserved for advanced disease stages.
Evaluation for Stem Cell Therapy Eligibility
Not all MDS patients are candidates for stem cell transplantation. A detailed evaluation is conducted to assess:
- Patient age and overall health
- Organ function (heart, lungs, liver, kidneys)
- Disease risk category
- Availability of a suitable donor
Comprehensive assessments ensure that stem cell therapy offers more benefits than risks for the individual patient.
Advanced Diagnostic Approach at Specialized Centers
At institutions like Liv Hospital, diagnosis and evaluation of MDS follow international clinical guidelines and incorporate cutting-edge diagnostic technologies. Patients benefit from coordinated care involving hematologists, pathologists, geneticists, and transplant specialists.
For a deeper medical overview of diagnostic protocols, you can explore the dedicated page on Stem Cell Myelodysplastic Syndrome Diagnosis and Evaluation, which outlines advanced assessment methods used in specialized stem cell programs.
Emotional Well-being and Long-Term Monitoring
Receiving an MDS diagnosis can be emotionally challenging. Alongside medical evaluation, patients are encouraged to focus on mental well-being, nutrition, physical activity, and stress management. Long-term follow-up includes regular blood tests, bone marrow assessments, and lifestyle adjustments to support overall health.
For insights into maintaining emotional balance and healthy living during long-term medical care, trusted wellness platforms like live and feel can offer supportive guidance and lifestyle-focused resources that complement clinical treatment.
Final Thoughts
Stem Cell Myelodysplastic Syndrome diagnosis and evaluation is a meticulous, multi-step process that lays the foundation for effective treatment planning. With early detection, advanced diagnostic tools, and expert evaluation, patients can access personalized care pathways that improve outcomes and quality of life. Choosing a specialized center ensures that every diagnostic detail is carefully analyzed, supporting informed decisions about stem cell therapy and long-term management.
Keep an eye for more latest news & updates on Down Uk!